Android Debug Bridge is a command-line tool that facilitates performing different actions such as installing or uninstalling apps, entering text, capturing screenshots, etc. on an Android device. I often use some adb commands to assist me during testing. Here's a list of adb commands that I commonly use:
Listing attached devices
- Command to list all the devices that are connected to the adb server:
adb devices - This command prints the serial number and the state of the device.

- If many devices are attached and we want to tell them apart, we could run the command with
-loption to list more details about the device.adb devices -l - This command shows us the device, it's model, etc.

Installing apps
- Apps can be installed on devices by giving the path to the
.apkfile:adb install <path_to_apk>.apk - If multiple devices are attached, running the command results in an error.

- In such cases, the serial number of the target device should be specified using the
-soption. The serial number is obtained by runningadb devices.adb -s <serial_number> install <path_to_apk>.apk
-s <serial_number>can be used in various adb commands when we want to target a specific device among a list of attached devices.
Listing packages
- Package Manager tool within the adb shell can be used to list all packages that are installed on the device:
adb shell pm list packages grepcan be used to list just specific packages that match the search term.
- This package information will be useful in a few other commands
Launching an Activity
- Activity names for a given package can be found using the command:
adb shell dumpsys package | grep <package_name> | grep Activity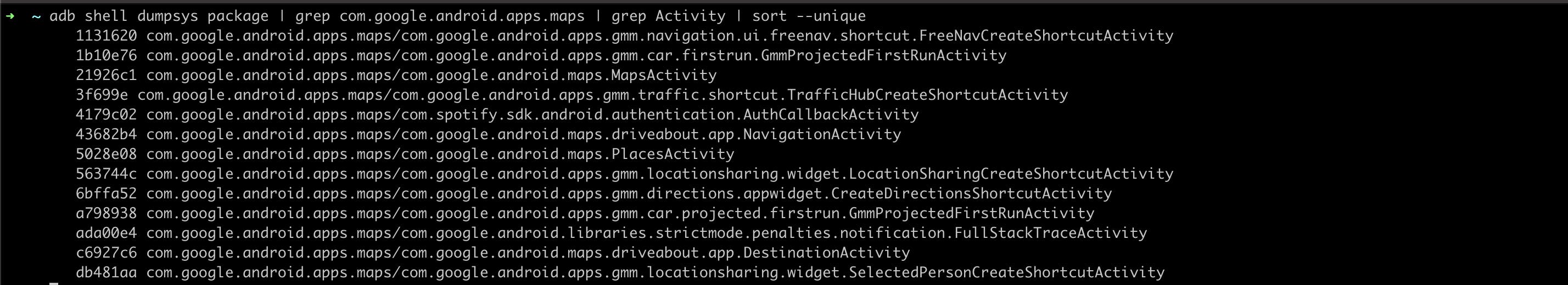
- Activity can be launched using the command:
adb shell am start <package_name>/<activity_name> - An example:
adb shell am start com.google.android.apps.maps/com.google.android.maps.MapsActivity
Opening URL in the browser:
- Activity manager tool can be used to open a URL in the Browser:
adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "<some_url>" - Example:
adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "https://developer.android.com/docs"
Entering text
- Command to enter text in a text field that has
focus:adb shell input text "<some_input>"
- Some characters like
!,&,(, etc. would need to be escaped with backslash (\) in the input text command.adb shell input text "\!\&\(\)\<\>\*\|"
Pressing home button
- KEYCODE_HOME keyevent can be used to emulate pressing the home button:
adb shell input keyevent KEYCODE_HOME
Killing an app from app switcher
- A series of keyevents can be used to kill an app from the app switcher:
adb shell input keyevent KEYCODE_APP_SWITCH adb shell input keyevent KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN adb shell input keyevent DEL
Clearing app data
- Command to clear app data:
adb shell pm clear <package_name> - In this example, Google Chrome has 4 tabs open. When app data is cleared and activity is launched again, the
Terms of Servicepage (page shown on first launch) is shown indicating that the app cache and data are cleared.
Capturing screenshot
- Commands to capture screenshot and pull it to the host machine:
adb shell screencap /sdcard/<screenshot_name>.png adb pull /sdcard/<screenshot_name>.png
Capturing videos
- Command to start recording screen:
adb shell screenrecord /sdcard/<some_video_name>.mp4 - After performing actions on the device, to stop the video recording,
ctrl + cneeds to be pressed. - To pull the recorded video to the host machine:
adb pull /sdcard/<some_video_name>.mp4
Viewing app logs
- Command to view logs:
adb logcat
Accessing app data directory
- To be able to access the data directory of a
debuggable app, the following commands can be run:adb shell run-as <package_name>
Uninstalling app
- Command to uninstall an app:
adb uninstall <package_name>